Some more eco-friendly options, at least with regards to emissions, existed for a long time, and one of them is hydro energy. But what exactly is hydro energy and how does it work and more importantly, is it really a viable environmentally-friendly alternative?
How does hydro energy work
Hydropower plants use water and gravity to produce electricity and the way they work is fairly simple: a turbine converts the kinetic energy of the falling water into mechanical energy, which is further converted by a generator into electric energy.
Hydro plants vary in size depending on how many people they were designed to serve, with micro-hydros designed to serve a few homes being the smallest, and one of the largest being the Hoover Dam that provides electricity for millions of people.
What are the components of a hydro plant
Most hydro plants are essentially made of four components, the first one being the dam, which is designed to raise the water levels, so we can have falling water, but it also has another important role in the way it can control water flow. The reservoir that is formed with the help of the dam is considered as stored energy.
Then comes the turbine, which just like tidal turbines, uses the kinetic energy of water in order to spin the blades, which turns the kinetic energy into mechanical energy.
The next component is the generator, which is connected through a shaft to the turbine, which spins the generator that is responsible for converting the mechanical energy into electricity.
Lastly, there are the electricity lines, which have the role of transporting the resulted energy to the people.
How can hydro plants produce more energy
Generally speaking, and you probably saw this coming, the amount of electricity a specific hydro plant can produce depends on two factors, how far the water falls (how tall the dam is) and how much water flows into the plant.
The largest hydro plants in the world
With this is mind, lets take a few examples of hydro plants around the world to see their rated capacity.
For instance, the Hoover Dam hydro plant in the USA, which is one of the largest in the world construction wise, has a rated capacity of 2.080 megawatts (MW), while Iron Gates I, a Romanian hydro plant located on the Danube river, has a capacity of 1.167 MW of capacity.
The largest hydro energy plant in the world resides in China and it is called Three Gorges Dam, and currently has the biggest capacity of all hydro plants in the world, by quite a bit as well.
To put things into perspective, the Itaipu Dam hydro plant in Brazil and Paraguay has a capacity of 14.000 MW, while Three Gorges in China has a whopping 22.500 MW of capacity, although over the course of a year, both plants produce about the same amount of electricity, due to seasonal fluctuations in the Yangtze River.
This means that the Three Gorges has a significantly higher capacity than Itaipu, its extra capacity being more than the largest hydro plant in the USA, called Grand Coulee Dam, which has a capacity of 6.800 MW.
The benefits of hydropower
Hydropower is a clean source of energy, as it doesn't emit gases in the atmosphere, which is a significant advantage in its own, but it is not the only one.
Water is one of the seemingly never ending resources on our planet, so technically, hydropower is a renewable type of energy, which is a big advantage when it comes to sustainability.
Hydroelectric power can also be used by many countries around the world that have access to water, so it can be considered a reliable domestic resource of energy.
Impoundment hydropower, also known as the reservoir, allows not only for electricity generation, but also for recreational activities, such as fishing, swimming and boating.
Hydroelectric power is also flexible, considering that hydro plants can reach maximum output very quickly, which is especially useful in the case of disruptions of major electricity outages. Because water flow is constant, we don't have to worry about having the main resource to produce energy, which in this case is water.
Hydropower is also an affordable type of energy generating source, and also has the benefit of being fairly durable.
Bridges, tunnels and dams can also be used as a way to mitigate construction costs, since they can be used to build a hydro plant.

Drawbacks of hydro plants
Perhaps the biggest downside of hydropower and hydro plants is the way they affect the environment. For example, building a dam for a hydro plant requires significant environmental changes, which affects the animals and plants and even human settlements in some cases.
Also, if there are not any in the specific place, power lines will also have to be constructed, which has a further environmental impact.
The quality of the water is affected as well, since water flow is limited, which in turn lower oxygen levels. Some species of fish might not be able to adapt do this change, and this could have more severe consequences in the natural food chain.
It sometimes forces people to move, which has happened a few times in the past, in order to facilitate the construction of dams, which are mostly necessary to build a hydro plant.
They can also be expensive to build, if there isn't an existing structure to support the hydro plant in the first place, like a dam or a bridge.
Since the 1950s, it is estimated that around 2 trillion dollars were spent in dam constructions around the world, most of which were built for hydro plants.
Hydro energy in Romania
There are multiple hydro plants in Romania, the biggest one being Iron Gates I, with an installed capacity of 1.167 MW, and the total hydro energy output of the country is 6 gigawatts (GW). Still, Romania has the potential to harvest more hydro power, as the installed capacity of hydro power accounts for nearly 30% of the country's total electricity output.
The estimated additional hydro power capacity that could be installed in Romania is about 9 GW.
Vidraru Dam Hydro Plant is one of the largest in the country as far as construction size goes, and it is an example of how a hydro plant, which produces 200MW of power in this case, can also bring touristic benefits, as it is one of the most important touristic attractions in the country.
Lake Vidraru is also an important touristic and recreational location that was resulted in the making of the hydro plant.
The Vidraru hydro plant is being used since 1966, and at that time it was the fifth largest hydro plant in Europe and the ninth in the world regarding the size of the construction.
Smaller Romanian hydro power plants include Lotru-Ciunget Hydroelectric Power Station, with an installed capacity of 800 MW, Râul Mare Hydroelectric Power Station, with 335 MW, and Iron Gate II Power Station, with a potential power output of 321 MW.

As the world is looking to reduce carbon emissions and still provide enough electricity for the population, there is an increasing need for sustainable and clean sources of energy.
Hydro energy could be a potential candidate, despite the drawbacks, since it can bring green energy in large quantities with a fairly minimal environmental footprint compared to other traditional sources of energy.
 Mihai - Cristian Ioniță
Mihai - Cristian Ioniță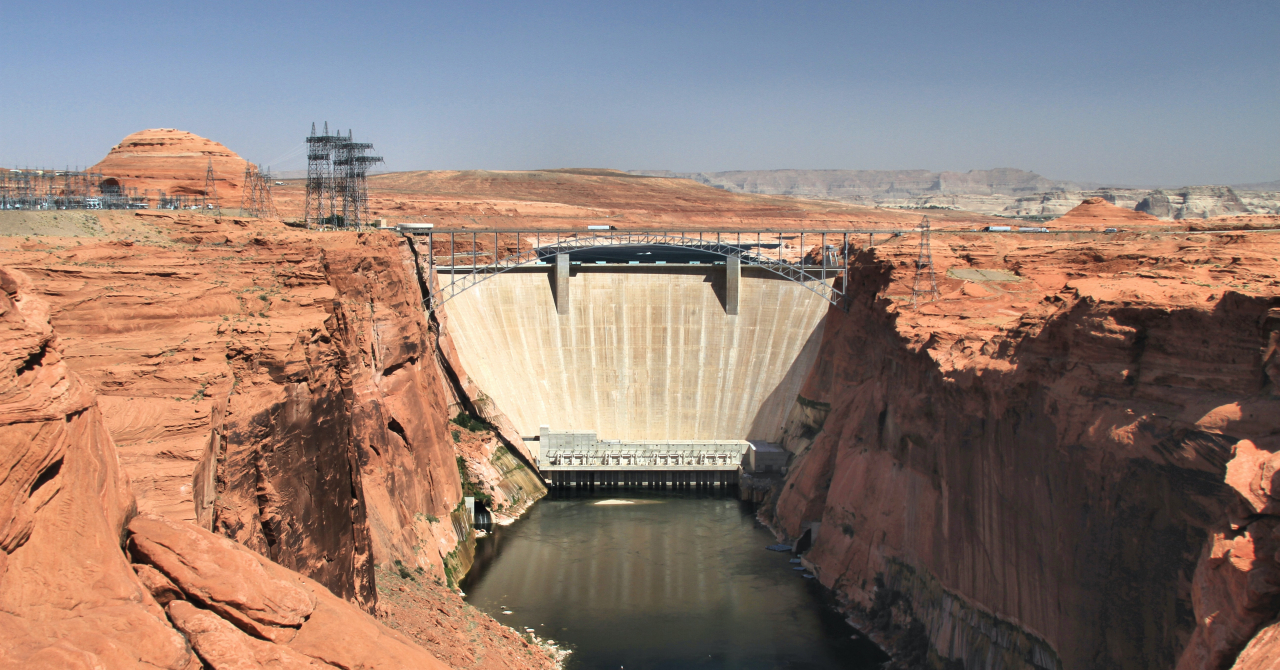











Any thoughts?