What are extreme weather events
Extreme weather events can be defined as unusually severe climate events that happen in certain conditions and that can affect a large number of people, from cities to entire regions of a country.
Despite not lasting more than a few days at a time, most of the time, extreme weather events have the power to destroy communities and even ecosystems and some examples of extreme weather events are tornadoes, heat waves, tsunamis and floods.
What causes extreme weather events
Extreme climate events happen during a sudden change of the weather in a certain area, which can determine the apparition of dangerous phenomena.
Although these events happened in the past, human activity has started to "fuel" the rate of apparition of extreme climate events.
Burning fossil fuels, whether it's in the transport or energy sector, is one of the main contributors to global warming, which in turn causes heat waves, cyclones or even droughts.
Some extreme events are not depending on us, such as earthquakes and tsunamis, which appear as a result of earthquakes that happen on the coast or the sea.
Extreme weather events happening from natural causes are fairly rare, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) says that humankind is to blame for most of the weather disorders that we are facing today.

Increasing wildfires that burn in more areas and for longer, droughts and unbearable heat, all of these are fueled by the greenhouse gas emissions that we release from various industries.
Since June and throughout August, parts of Europe, thw US, the Middle East and North Africa have been affected by wildfires. According to the data from the EU, nearly 660.000 hectares of land from the European countries have been destroyed by wildfires since the beginning of this year.
Types of extreme climate events
There are a few types of extreme weather events that can occur, some of them only in certain areas around the world, but one of them is present pretty much all over the place.
Heat waves and global warming in general is a phenomenon that isn't extreme in itself, but it can lead to unusual events.
Some of those are the increase in the rate of wildfires and increasingly hot temperatures in most regions on Earth, which causes more desert-like areas to appear and even glaciers to melt.
This is one result of climate change that takes its toll more and more on the planet and the ecosystems each year, instead of doing all the damage at once.
Freeze waves are the opposite of heat waves, meaning that they bring a wave of cold air that can cause serios damage to agriculture crops and even the infrastructure of unprepared cities or regions.
According to the IPCC, these kinds of events aren't as likely to happen as they once were, but they shouldn't be ignored, as some regions might still face them due to climate change.
Floods are another type of extreme climate phenomena that can seriously affect large areas.
Despite global warming causes the rise of temperatures that in return mean more droughts, torrential rains can still happen and these violent storms can bring large quantities of water in a short amount of time.

Sometimes, they are accompanied by strong winds which can cause damage to trees, homes and the infrastructure of a certain place.
Earthquakes are a less common type of extreme event, although it depends on the region, and they are caused by the crashing of tectonic plates, which makes the Earth's surface to shake.
They can be very small in intensity, meaning that we don't even feel them, but they can also be very violent and deadly.
If they happen out on the ocean or the sea, they can even generate tsunamis, and when combined, they can be some of the deadliest extreme weather events in the world.
The deadliest extreme climate events in history
Although they do damage every time they occur, on some occasions these types of events can be so deadly that they remain regarded in history as great catastrophes.
The 1970 Bhola Cyclone was an extreme climatic event that went down in history as one of the deadliest after it hit what was at the time East Pakistan.
The strongest winds were measured at some 205 km/h and there were also major floods, which caused many low-lying islands to go underwater.
The total death toll is estimated at anything between 300.000 and 500.000, besides material loss.
One of the deadliest earthquakes in history took place in the Shaanxi province in China, back in 1556.
Although it happened quite a while back, the event is pretty well documented and it is estimated that around 1.000 kilometers of land was turned to nothing but rubble after the catastrophe.

Experts in China believe that around 830.000 people lost their lives in this natural disaster.
The 1931 Yangtze River Floods are regarded as some of the deadliest extreme phenomena in recorded history.
Heavy rainfall that happened in China in the summer of 1931 caused the Yangtze River to overtop its banks and flood around 180.000 square kilometers of land, while the death toll is estimated between 2 million and 3.7 million people.
Strange extreme weather events
Extreme weather events don't have to always bring large death tolls, but they still have the power to baffle scientists and the locals.
Greenland's fires and rain over its ice cap peak are two fairly recent events that surprised everybody.
In 2017, several wildfires broke out on the western side of Greenland, a series of events that definitely took scientists by surprise, as the region is mostly known for its ice caps and snowy landscape.
At the same time, a testimony of global warming is the fact that, in 2021, rain was observed over Greenland's highest point, a worrying sign for the researchers at the National Snow and Ice Data Center.

The time Siberia warmed to 38 degrees Celsius was recorded in June, 2020, as the town of Verkhoyansk, located just 418 kilometers south of the Arctic coast, registered the highest temperatures ever in the region.
In fact, according to scientists, this is the highest temperature ever recorded north of the Arctic Circle and the event caused wildfires that spanned across a region larger than the size of Greece.
How to stop extreme weather events
The truth is that there are some extreme phenomena that we can't just stop happening, such as earthquakes and tsunamis.
Some of them, such as floods, tornadoes and droughts are still bound to happen, but by becoming more sustainable and by burning less fossil fuels, we can ensure that they don't reach their worst magnitude and are less likely to destroy entire communities or ecosystems.
Also, by coming up with proper evacuation plans and building protective infrastructure, authorities can make sure that, in case a natural calamity will happen, there will be as little victims as possible as a result of such extreme weather events.
 Mihai - Cristian Ioniță
Mihai - Cristian Ioniță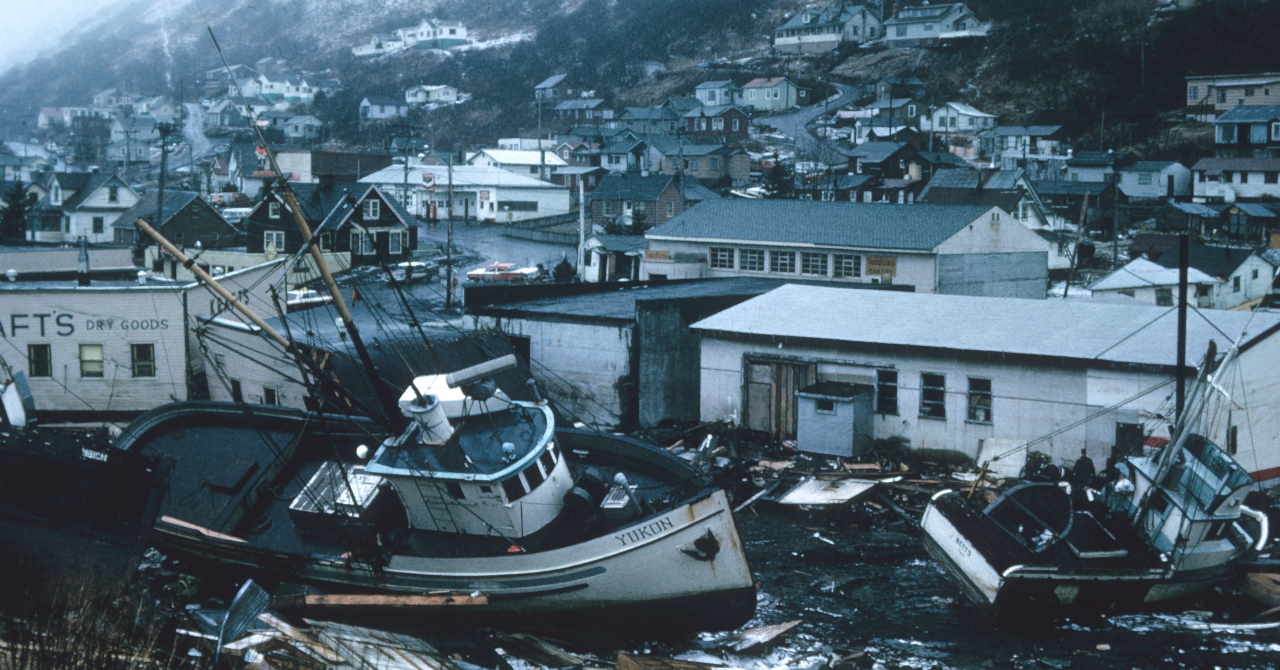











Any thoughts?